CONTINUATION OF LIFE .....
In today's topic I would cover topics about the mechanism of determination of sex in humans
Before moving on to the mechanism of sex determination , i would like to make you all familiar to some important terminologies :
- Gene- basic unit of heredity
- Somatic cells - All body cells except reproductive cells
- Gamete- reproductive cells
- chromosome - elongate cellular structure composed of DNA and protein, they are vehicles which carry DNA in cells.
Lets go into the details of chromosomes
CHROMOSOMES
Chromosomes are special cellular structures which are formed of highly colied structure DNA which consists of genes. Chromosomes contain the genetic material of the cell which passes on from one generation to next generation.
Chromosomes are of basic two types :
- 22 pairs of Autosomes or somatic chromosomes
- and 1 pair of Allosomes or Sex chromosomes
Allosomes or Sex chromosomes are the ones which are involved in the process of determination of sex of an individual and Autosomes are the ones which have their role in the general body functions .
Sex chromosomes in case of mammals are of two different types :
XX in case of females and XY in case of males
These chromosomes are present in the reproductive cells , hence they undergo meiotic division .
Females are Homogametic as they have XX chromosomes and males are heterogametic as they have XY chromosomes , that is the human sperm present in males have both X and Y chromosome , Therefore males are responsible for the process of sex determination of the offspring and not the female .
Furthermore, lets go into the details of the structure of sperm in males and ovum in the females.
HUMAN SPERM

Structure of sperm
- The mammalian sperm cell consists of a head, midpiece and a tail .
- The head contains the nucleus with densely coiled chromosomes surrounded by an acrosome.
- The midpiece has a central core of spiral shaped mitochondria.
- The tail haleps in propellation pf the sperm
HUMAN OVUM
- The mammalian ovum consists of an outer corona radiata and inner zona pellucida.
- the cytoplasm of the ovum cell is known as ooplasm which shows the presence of a pronucleus.

Structure of ovum
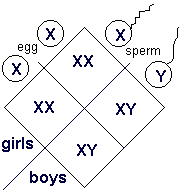
INHERITANCE OF XY CHROMOSOMES
- During gamete formation, the normal diploid chromosome is halved. This is called the haploid condition.
- All the eggs of a female have 22+X.
- A male produces two types of sperms, one type bears 22+X composition and the other 22+Y .
- Therefore, in many 100 sperms , 50 have Y chromosomes and 50 X chromosomes.
- Any one of the two types of sperms can fertilize the egg.
- If a Y bearing sperm fertilizes the egg, the zygote has the 44+XY composition, and the resulting foetus grows to be a boy.
- When an X- bearing sperm fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote has the 44+XX composition, resulting into a girl.
- All the children inherit one X chromosome from the mother.
- Therefore, sex is always determined by the other sex chromosome that they inherit from the father.
- One who inherits the X chromosome of the father is a girl, while one who inherits the Y chromosome of the father is a boy.

This video will help you all to understand the mechanism of sex determination better
Thankyou
*kindly give your suggestions *

No comments:
Post a Comment