DISEASES OF REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
DISEASES OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE-
- Inflammation of the female reproductive organs often dut to a sexually transmitted infection.
- Most common between the ages of 15 to 24.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease is a common cause of pain in the pelvic region in women.
- The infection spreads upwards from the vagina to the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Also takes place due to insetion of intra-uterine contraceptive device.
SYMPTOMS:
- Pain in pelvic region.
- Fever
- An abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Heavy or prolonged periods.
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Tiredness
- nausea, vomiting
- damaged fallopian tubes
- Inflammation of the female reproductive organs often dut to a sexually transmitted infection.
- Most common between the ages of 15 to 24.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease is a common cause of pain in the pelvic region in women.
- The infection spreads upwards from the vagina to the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Also takes place due to insetion of intra-uterine contraceptive device.
SYMPTOMS:
- Pain in pelvic region.
- Fever
- An abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Heavy or prolonged periods.
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Tiredness
- nausea, vomiting
- damaged fallopian tubes

pelvic inflammatory disease
video to understand pelvic inflammatory disease
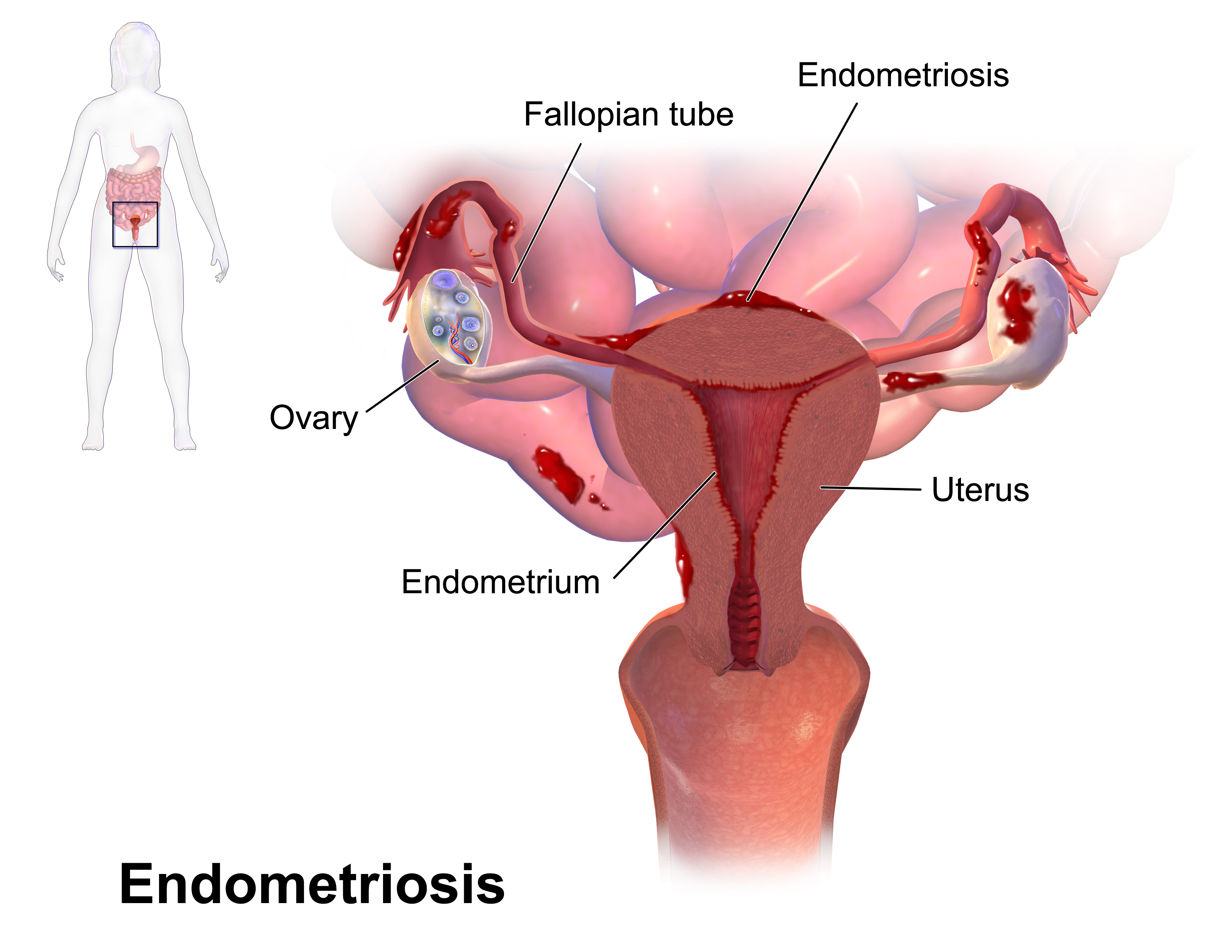
2. ENDOMETRIOSIS-
- A condition in which endometrial tissue, which lines the uterus but in this case it is attached to other organs in the abdomen.
- Common between the ages of 30 and 45.
- The lining of the uterus, known as endometrium , is normally shed once a month during menstruation and then regrows.
- in endometrium, some pieces of the lining are attached to organs in the pelvic cavity, such as the ovaries and the lower intestine.
- These pieces of endometrial tissue react to the hormones of the menstrual cycle and bleed during menstruation.
- The blood cannot leave the body through the vagina and this can cause irritation of the surrounding tissues, leading to pain in the abdomen and eventually scarring.
- irritation of the ovaries may lead to blood filled cysts.
- it is a common condition, affecting as many as 1 in 5 women of childbearing age.
- Women who do not have children until they are in their 30s and those who remain childless are more likely to develop the condition.
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in lower abdomen, which often becomes more severe just before and during menstrual periods.
- Heavier menstrual bleeding
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- If endometrium grows on the lower intestine, you may develop diarrhoea or constipation, pain during bowel movements, and in rare cases, bleeding from the rectum during menstruation.
video for endometriosis
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME -
- Multiple , small fluid filled cysts in the ovaries associated with a sex hormone imbalance.
- Affects females of childbearing age.
- Sometimes runs in families.
- Many women have multiple fluid filled cysts in their ovaries but most of these women do not have polycystic ovary syndrome, which is the presence of multiple ovarian cysts associated with an imbalance of the sex hormones and certain other characteristics , such as acne , excessive body hair, and menstrual irregularities.
- Higher levels of male sex hormone testosterone, may prevent ovulation, thus reducing fertility.
- The underlying cause of PCOS cause is increased resistance of body tissues to be hormone insulin that is a feature of the syndrome and is thought to play an important part.
- To compensate for the increased insulin resistance, the pancreas produces excessive insulin, ehich in turn, may lead to over production of testosterone , high levels of which disrupt normal functioning of the ovaries.
SYMPTOMS-
- Infrequent or absent periods
- Obesity
- excessive hair growth on the face, around the nipples or on the lower abdomen.
- Thinnig of the hair on the head.
- Long lasting acne.
- Women with PCOS have an increased risk of diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and cancer of the uterus.

video for PCOS
FIBROIDS-
- Common, noncancerous tumours that grow slowly within the muscular wall of the uterus.
- Most common between the ages of 35 to 55.
- fibroids are non-malignant growths in the uterus that consist of muscular and fibrous tissue.
- Small Fibroids may not cause problems but larger ones may affect menstrution or fertility.
- Fibroids occur singly or in groups and may be small as a pea or as big as a grapefruit.
SYMPTOMS-
- Prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Abdominal pain during periods
- Heavy bleeding during periods.
- Heavy blood loss may lead to anaemia causing pale skin and tiredness.
- Large fibroids may distort the uterus which can sometimes result in infertility and possibly in recurrent miscarriages.
- During pregnancy a large fibroid may cause the foetus to lie in an abnormal position.
- Fibroids may also press on the bladder causing a need to pass urine often, or on the rectum, causing back pain.

Video for fibroids
CERVICAL INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA -
- Changes in the surface cells of the cervix that may become cancerous.
- Most common between the ages of 25 to 35.
- There are 3 grades, depending on the severity of the changes in the abnormal cells; mild, moderate and severe.
- Mild CIN returns to normal state by itself but moderate or severe CIn may progress to the concer of cervix, if not treated.
- It is caused usually due to exposure to some types of human papillomavirus.
- Other risk factors for the development of CIN include unprotected sex at an early age and unprotected sex with many partners because these activities are associated with an increased risk of acquiring HPV infection.
VULVOVAGINITIS-
- Inflammation of the vulva and vagina, causing itching and soreness.
- There may also be pain during sexual intercourse and a discharge from the vagina.
- Most cases of vulvovaginitis are caused by an infection, either with the fungus Candida albicans, or the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis, which is the cause of the sexually transmitted infection trichomoniasis.
- Women with diabetes mellitus have an increased risk of fungal vulvovaginits.
- The condition may be caused by irritation from perfumed bath products, detergents, deoderants, or contraceptive creams.

video of vulvovaginitis
DISEASES OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Epidermal cysts -
- More common over the age of 40.
- Epididymal cysts or spermatoceles, are harmless fluid - filled sacs that form in the epididymis, which stores and transports sperm away from the testis.
- Small epididymal cysts are common, particularly in men over the age of 40.
- The cysts develop slowly and are usually painless.
- In many cases, there are multiple cysts, which can be felt as distinct, painless swellings like a tiny bunch of grapes on top of and behind the testis.

Torsion of the testis -
- Twisting of the testis within the scrotum, causing severe pain.
- Most common between the ages of 12 and 18 but can occur at any age.
- Each testis is suspended in the scrotum on a spermatic cord.
- The spermatic duct and the blood vessels that supply the testis are contained in the spermatic cord.
- If the spermatic cord becomes twisted, the flow of blood to the testis is restricted, causing severe pain in the scrotum.
- Torsion of the testis usually affects only one of the testes.
- if sometimes occurs often strenous activity but may develop for no apparent reason, even during sleep.
- Torsion of the testis most commonly occurs during adolescence, but it can develop at any age.
- The condition is potentially serious , torsion may result in permanent damage to the testis if not treated immediately.
SYMPTOMS-
- Sudden pain in the scrotum that tends to increase in severity.
- Pain in the groin and lower abdomen.
- Redness and extreme tenderness of the scrotum on the affected side.
- The severity of pain can cause nausea and vomiting.
BALANITIS -
- Inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin.
- More commin in children.
- In addition, there may be a discharge , and a rash may develop.
- The disorder can be caused by a bacterial infection, a fungal infection such as thrush or an allergic reaction.
- It may also be due to a sexually transmitted infection such as the protozoal infection trichomoniasis.
- A tighter than normal foreskin may increase the risk of infection by preventing effective cleaning of the glans.
- Men with diabetes mellitus are more susceptible to the condition because their urine contains high level of glucose, which can encourage growth of micro organisms.
- This leads to infection and inflammation at the opening of the urethra.
- Excessive use of antibiotics can increase the risk of a fungal infection by temporarily lowering the body's natural defences against this type of infection.
- The condition may also occur as a result of sensitivity of the penis to certain chemicals, such as those found in some condoms, contraceptive creams, detergents and washing powders.

BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY -
- It is characterized by proliferation of the cellular elements of the prostate.
- Chronic bladder outlet obstruction secondary to BPH may lead to urinary retention, renal insufficiency, recurrent urinary tract infections, gross hameturia, and bladder calculi.
SYMPTOMS -
- Urinary frequency
- urinary urgency
- Hesitancy
- Incomplete bladder emptying
- Straining
- Decreased force of stream
- Dribbling

* Do Give your suggestions *
Thamkyou

No comments:
Post a Comment