INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN)

What is Skin ?
The skin is the outermost covering of the body. It is stretched all over the body in the form f a layer .
Functions of Skin
1. Protection
* It protects the underlying tissues from mechanical shocks
* It holds the body fluids inside and prevents excess loss of water by evaporation.
* It prevents the entry of harmful substances
* It protects the body from the harmful ultraviolet radiations
2. Sensation
Our skin is a sense organ od touch , pain , pressure and heat
3. Temperature Regulation
The skin prevents loss of heat in cold weather and facilitates loss of heat in hot weather.
4. Storage of food
The skin stores food in the special layer of fat cells.
5. Excretion
The skin eliminates wastes in the form of sweating
6. Synthesis of vitamin D
The skin synthesize vitamin D when exposed to sunshine .
LAYERS OF SKIN
1. THE EPIDERMIS
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin which we can see through naked eyes everyday.
The upper layer of epidermis consists of a layer of dead cells and the lower layer of epidermis consists of a basement membrane .
The basement membrane consists of specialised cells called as melanocytes .
These melanocytes divide continuously .
These melanocytes consist of a pigment called melanin.
Melanin is a pigment which imparts colour to your skin.
More the melanin , more the person has a darker skin.
Melanin is the pigment which acts as a sheild and provides protection from the harmful UV rays .
Hence, darker the person, more safer from the ultraviolet radiations and hence less susceptible to skin cancer.
Melanin under extreme sunshine underoes tanning of skin which actually prevents us from harmful UV rays.
Tanning process is stimulated by the hormone MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone ) which is secreted by Intermediate Pituitary Gland .
The dead cell layer of the epidermis consists of keratinocytes which contains a protein called keratin.
This keratin forms a tough protective layer , hence acts as a natural barrier and prevents entry of many harmful substances.
The epidermis also consists of Langerhan cells which attacks the harmful bacteria and viruses that enter the skin.
The dead cell layer of epidermis sheds and gets replaced after every 20-30 days.

The dead cell layer is the stratum cornuem and and melanin part is stratum basale .

2.THE DERMIS
Below the epidermis is the dermis layer which is divided into two regions :
1. The upper papillary region
2. The lower reticular region
Upper papillary layer -
It is made up of loose connective tissue .
Lower reticular layer -
It is made up of tightly packed tissues
The dermis consists of strong collagen and elastin fibres pierced by blood vessels.
These blood vessels help to regulate the temperature by increasing the blood flow to the skin when you are hot and constricting the blood vessels when your cold and need to keep calm.
The dermis consists of a network of nerves and receptors which help us to sense touch , feel , pain and pressure.
The dermis consists of skin derivatives such as oil glands or sebaceous glands, hair follicles and sweat glands.
Dermis also acts as a cushion on an injury.

The dermis consists of a network of nerves and receptors which help us to sense touch , feel , pain and pressure.
The dermis consists of skin derivatives such as oil glands or sebaceous glands, hair follicles and sweat glands.
Dermis also acts as a cushion on an injury.

Skin Derivatives
The derivatives of skin includes sweat glands, nails, sebaceous glands, nails , hair follicles and mammary glands .
1. SWEAT GLANDS
Sweat glands are a dermal derivative of the skin and are of two types :
a) Eccrine sweat glands B) Apocrine sweat glands
They are present all over the body. They are concentrated in the armpits.
The sweat produced by it cools down The sweat secreted is slightly thicker and is
the body when temperature rises. milky, which is released during stress.
The secretions of this gland produces body
odor which causes the bacteria to multiply
and their waste gives rise to unpleasant
smell.
The eccrine glands open up directly into Apocrine glands release sweat at the root
skin's epidermis. of hair follicles.


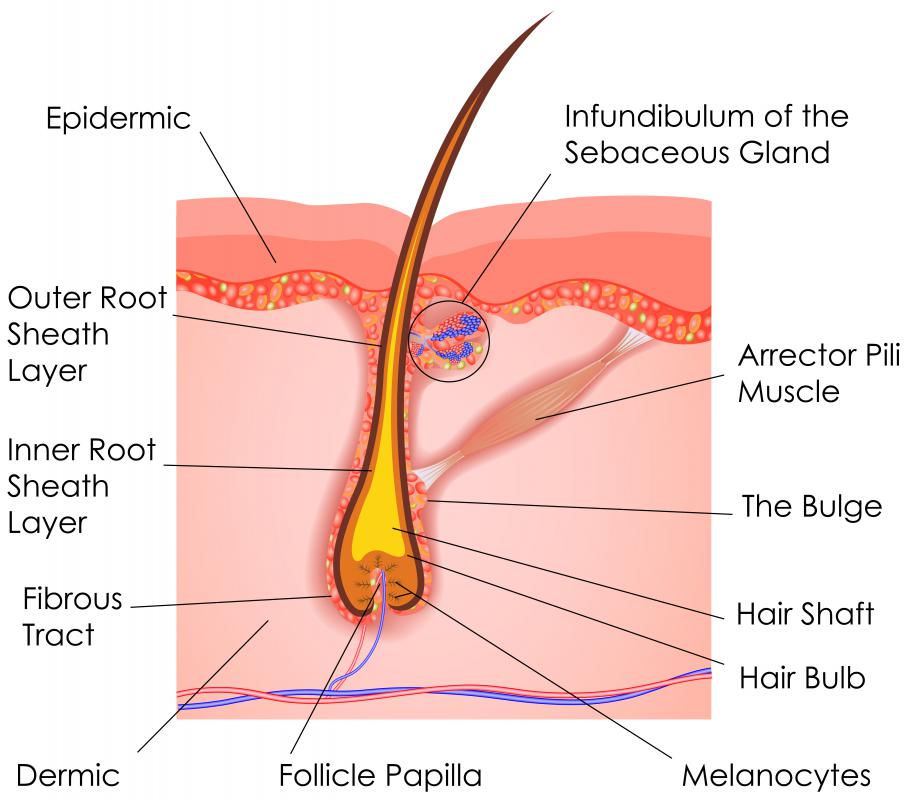
SEBACEOUS GLANDS (OIL GLANDS)
Sebaceous glands are small oil producing glands . These are attached to the hair follicles and release sebum or oil in thr follicles and then on the surface of the skin. These glands are abundant on the scalp and the face.
The sebum forms a greasy surface which keeps the skin flexible and prevents the loss of large amounts of water.
These glands are involved in the development of a common adolescent skin disease known as acne.

The sweat produced by it cools down The sweat secreted is slightly thicker and is
the body when temperature rises. milky, which is released during stress.
The secretions of this gland produces body
odor which causes the bacteria to multiply
and their waste gives rise to unpleasant
smell.
The eccrine glands open up directly into Apocrine glands release sweat at the root
skin's epidermis. of hair follicles.

SEBACEOUS GLANDS (OIL GLANDS)
Sebaceous glands are small oil producing glands . These are attached to the hair follicles and release sebum or oil in thr follicles and then on the surface of the skin. These glands are abundant on the scalp and the face.
The sebum forms a greasy surface which keeps the skin flexible and prevents the loss of large amounts of water.
These glands are involved in the development of a common adolescent skin disease known as acne.

HAIR FOLLICLES
It is a structure of skin from where the hair grows. The hair follicles are all over the body except the lips, palms, and soles.
The hair follicle has oe or two sebaceous glands which secrete sebum and lubricate the hair follicles. Apocrine glands help in lubricating the hair follicles of the armpits.
The hair follicle also consists of a errector pilli which is responsible to create goosebumps when contracted.
The papilla of the hair follicles consist of epithelial cells responsible fr hair growth and melanocytes which are responsible to impart colour to te hair.
NAILS
Nails are known as germinal matrix , a tissue lying beneath the skin behind the fingernail.
The matrix consists of nerves and blood vessels and supplied with the nutrients.

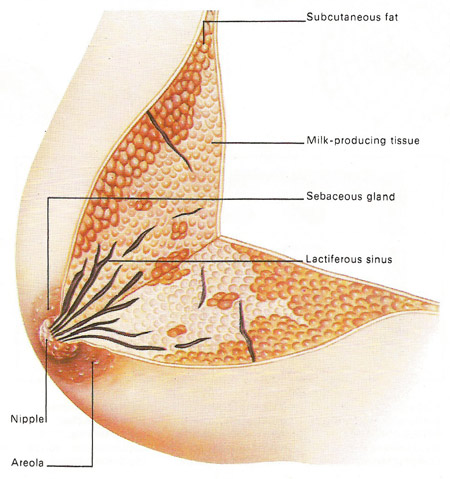
MAMMARY GLANDS
Mammary word comes from the word mammals. The mammary glands are the extensions of the apocrine sweat glands. Mammary glands develop in the females at the time of puberty under the influence of a female sex hormone estrogen.
The mammary glands are responsible for the secretion of milk for the new born offspring.
The milk oozes out of the breasts under the influence of hormones prolactin and oxytocin.
Derivatives of skin

Very thorough and informative..
ReplyDeleteThankyou aunty
ReplyDeleteThankyou aunty
ReplyDelete